Net Zero
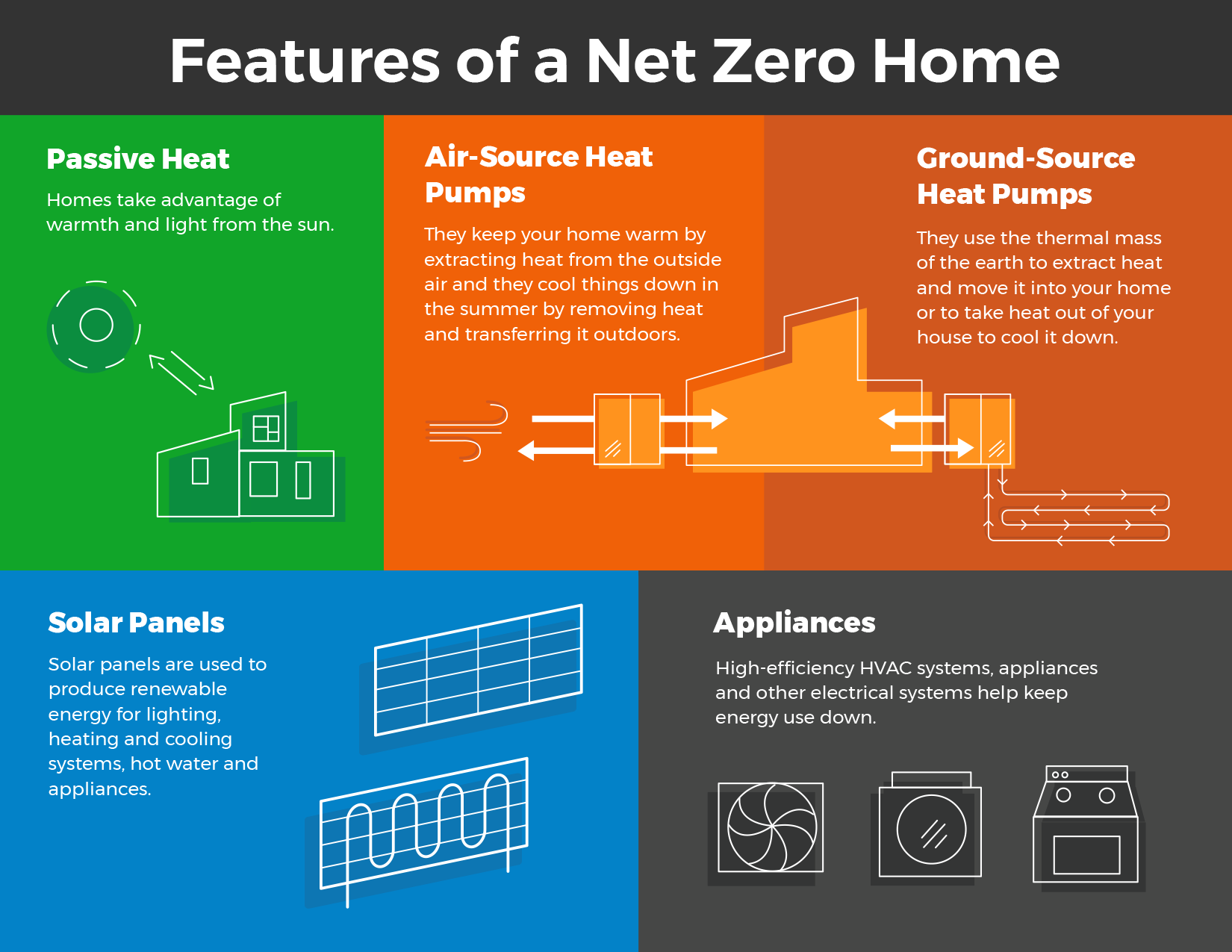
Net-zero energy buildings produce as much clean energy as they consume. They are designed to be much more energy-efficient than a typical new building, often using approaches like Passive House or the upper levels of the Step Code, and they use on-site (or near-site) renewable energy systems to produce the remaining energy they need. A net-zero energy-ready building is one that has been designed and built to a level of performance such that it could, with the addition of solar panels or other renewable energy technologies, achieve net-zero energy performance.
In Metro Vancouver, the most common method to achieving a net zero home is to add a grid-tied system of solar photovoltaic panels that may also include energy storage (batteries). This allows excess energy to be returned to the grid during the day through a process called Net Metering, offsetting energy that might need to be drawn from the grid at night (when demand tends to be higher). Geothermal energy is another excellent method of producing very consistent energy onsite. The cost to install geothermal piping underground can be fairly high, however it has a significant advantage over solar in that it has a much lower embodied carbon content. Wind turbines, hydro and biofuels are other ways to generate renewable power on or near the site that are locally used less commonly.